Page 107 - AERB
P. 107
0.1 m/s to 5 m/s. It was observed that time of onset hydraulics modelling. The results of Phase 1A have
of recombination is inversely proportional to forced been inter-compared and compiled. AERB, BARC,
circulation (counter current) velocity. NPCIL and IGCAR are participating in this exercise.
Specification for Phase 1C has been prepared and
7.1.6 CFD Simulation of Containment Hydrogen distributed to participants.
Distribution for 700 MWe PHWR
7.1.8 ISOMED Source Storage Cooling Analysis and
The main objective of this work is to study the Cooling Coil Design
distribution of hydrogen in containment for accident
scenario LOCA+LECCS+LMODC. The CFD ISOMED, the first irradiation plant for sterilization
simulation up to 17000 s was completed and there is of medical products, was set up in India at Trombay
uniform hydrogen volumetric concentration of 5.4% with the assistance of the United Nations Development
60
observed in containment above 120 m elevation (top of Programme (UNDP). In this facility, Co is used as the
FM vault plane). Diagonally opposite to FM vault, two source of radiation and the plant had been in operation
distinct layers of hydrogen concentration are observed. for more than four decades (since 1974). The radiation
Predictions show that hydrogen concentration of 3.5% source is housed in a concrete cell and this concrete is
and 2.5% by volume in upper and lower portions cooled by water circulating through the cooling coils
respectively. embedded in the concrete shield. For the assessment of
the cooling coil capability, a 3-D model of the concrete
7.1.7 Coupled Neutronics Thermal-Hydraulics Safety shield along with the steel liner was developed in multi-
Analysis for 540 MWe PHWR physics software COMSOL. Further, as the facility is
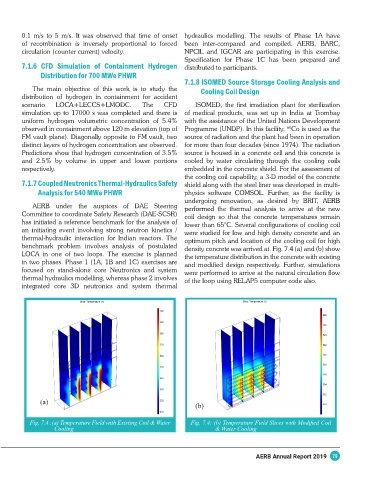
undergoing renovation, as desired by BRIT, AERB
AERB under the auspices of DAE Steering performed the thermal analysis to arrive at the new
Committee to coordinate Safety Research (DAE-SCSR) coil design so that the concrete temperatures remain
has initiated a reference benchmark for the analysis of lower than 65°C. Several configurations of cooling coil
an initiating event involving strong neutron kinetics / were studied for low and high density concrete and an
thermal-hydraulic interaction for Indian reactors. The optimum pitch and location of the cooling coil for high
benchmark problem involves analysis of postulated density concrete was arrived at. Fig. 7.4 (a) and (b) show
LOCA in one of two loops. The exercise is planned the temperature distribution in the concrete with existing
in two phases. Phase 1 (1A, 1B and 1C) exercises are and modified design respectively. Further, simulations
focused on stand-alone core Neutronics and system were performed to arrive at the natural circulation flow
thermal hydraulics modelling, whereas phase 2 involves of the loop using RELAP5 computer code also.
integrated core 3D neutronics and system thermal
(a) (b)
Fig. 7.4 :(a) Temperature Field with Existing Coil & Water Fig. 7.4: (b) Temperature Field Slices with Modified Coil
Cooling & Water Cooling
AERB Annual Report 2019 79