Page 108 - AERB
P. 108
7.1.9 Containment Thermal Hydraulics response of emergency exercise conducted at MAPS site. Thermal
KAPS-1 Small Leak Event hydraulic inputs required for assessment of source term
were derived from the existing analyses.
Containment thermal hydraulics analysis of KAPS-
1 following small leak has been carried out by Lumped 7.2.3 Analysis of Postulated Main Steam Line Break
Parameter (LP) code. The predictions are compared (MSLB) of 700 MWe PHWR
with the recorded plant data and NPCIL predictions and
are in reasonable agreement for the event. As part of independent verification, analysis
of MSLB with crash cool down was carried out. A
7.2 SEVERE ACCIDENT STUDIES postulated Double-Ended Guillotine Break (DEGB) has
been simulated in one of the main steam line inside
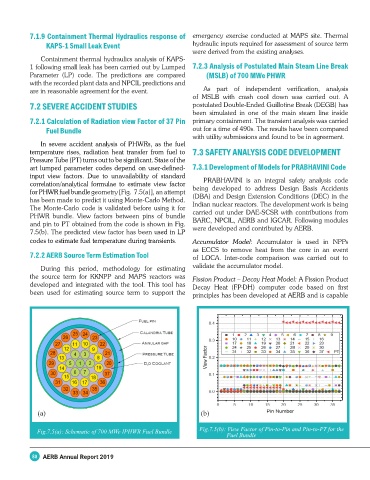
7.2.1 Calculation of Radiation view Factor of 37 Pin primary containment. The transient analysis was carried
Fuel Bundle out for a time of 490s. The results have been compared
with utility submissions and found to be in agreement.
In severe accident analysis of PHWRs, as the fuel
temperature rises, radiation heat transfer from fuel to 7.3 SAFETY ANALYSIS CODE DEVELOPMENT
Pressure Tube (PT) turns out to be significant. State of the
art lumped parameter codes depend on user-defined- 7.3.1 Development of Models for PRABHAVINI Code
input view factors. Due to unavailability of standard
correlation/analytical formulae to estimate view factor PRABHAVINI is an integral safety analysis code
for PHWR fuel bundle geometry [Fig. 7.5(a)], an attempt being developed to address Design Basis Accidents
has been made to predict it using Monte-Carlo Method. (DBA) and Design Extension Conditions (DEC) in the
The Monte-Carlo code is validated before using it for Indian nuclear reactors. The development work is being
PHWR bundle. View factors between pins of bundle carried out under DAE-SCSR with contributions from
and pin to PT obtained from the code is shown in Fig. BARC, NPCIL, AERB and IGCAR. Following modules
7.5(b). The predicted view factor has been used in LP were developed and contributed by AERB.
codes to estimate fuel temperature during transients. Accumulator Model: Accumulator is used in NPPs
as ECCS to remove heat from the core in an event
7.2.2 AERB Source Term Estimation Tool of LOCA. Inter-code comparison was carried out to
During this period, methodology for estimating validate the accumulator model.
the source term for KKNPP and MAPS reactors was Fission Product – Decay Heat Model: A Fission Product
developed and integrated with the tool. This tool has Decay Heat (FP-DH) computer code based on first
been used for estimating source term to support the principles has been developed at AERB and is capable
(a) (b)
Fig.7.5(a): Schematic of 700 MWe IPHWR Fuel Bundle Fig.7.5(b): View Factor of Pin-to-Pin and Pin-to-PT for the
Fuel Bundle
80 AERB Annual Report 2019