Page 109 - AERB
P. 109
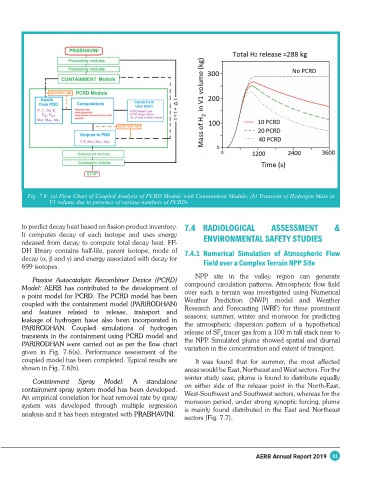
Fig. 7.6: (a) Flow Chart of Coupled Analysis of PCRD Module with Containment Module, (b) Transient of Hydrogen Mass in
V1 volume due to presence of various numbers of PCRDs
to predict decay heat based on fission product inventory. 7.4 RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT &
It computes decay of each isotope and uses energy ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY STUDIES
released from decay to compute total decay heat. FP-
DH library contains half-life, parent isotope, mode of 7.4.1 Numerical Simulation of Atmospheric Flow
decay (α, β and γ) and energy associated with decay for Field over a Complex Terrain NPP Site
699 isotopes.
NPP site in the valley region can generate
Passive Autocatalytic Recombiner Device (PCRD)
Model: AERB has contributed to the development of compound circulation patterns. Atmospheric flow field
a point model for PCRD. The PCRD model has been over such a terrain was investigated using Numerical
coupled with the containment model (PARIRODHAN) Weather Prediction (NWP) model and Weather
and features related to release, transport and Research and Forecasting (WRF) for three prominent
seasons; summer, winter and monsoon for predicting
leakage of hydrogen have also been incorporated in
PARIRODHAN. Coupled simulations of hydrogen the atmospheric dispersion pattern of a hypothetical
transients in the containment using PCRD model and release of SF tracer gas from a 100 m tall stack near to
6
PARIRODHAN were carried out as per the flow chart the NPP. Simulated plume showed spatial and diurnal
given in Fig. 7.6(a). Performance assessment of the variation in the concentration and extent of transport.
coupled model has been completed. Typical results are It was found that for summer, the most affected
shown in Fig. 7.6(b). areas would be East, Northeast and West sectors. For the
winter study case, plume is found to distribute equally
Containment Spray Model: A standalone
containment spray system model has been developed. on either side of the release point in the North-East,
An empirical correlation for heat removal rate by spray West-Southwest and Southwest sectors, whereas for the
monsoon period, under strong synoptic forcing, plume
system was developed through multiple regression is mainly found distributed in the East and Northeast
analysis and it has been integrated with PRABHAVINI.
sectors (Fig. 7.7).
AERB Annual Report 2019 81