Page 121 - AERB
P. 121
The shielding efficacy of both the advanced dose, the calibration curve obtained with the gamma
materials of interest are observed to be better than and neutron fields has been used (for MTS-6) in the
ordinary concrete for LWR spectrum. Samarium, which present study to give clear estimation of neutron dose.
has a higher thermal neutron absorption cross-section of The thermal neutron dose values measured using MTS-
149
40800 barns for Sm, shows predominant attenuation 6 and MTS-7 TL detectors were found to show the
behaviour compared to Boron with thermal neutron expected trends and good agreement with the theoretical
absorption cross-section of 3840 barns for B. The Monte Carlo simulations.
10
difference in weight fractions of Samarium and Boron
in respective shield materials also partly contribute to 7.8 STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND MATERIAL
the effect. STUDIES
7.7.11 Thermal Neutron Dosimetry using LiF:Mg,Ti 7.8.1 Studies for Mechanical Properties Evaluation
6
and LiF:Mg,Ti based Thermoluminescence of Zr-2.5%Nb PT Specimen
7
Detectors
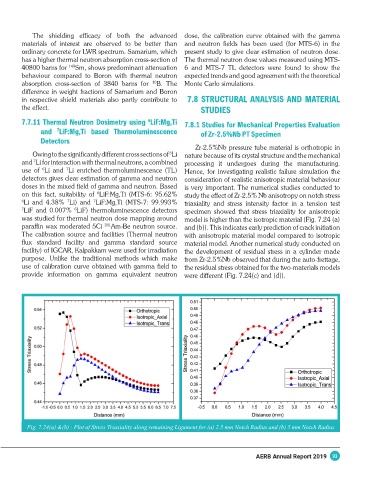
Zr-2.5%Nb pressure tube material is orthotropic in
6
Owing to the significantly different cross sections of Li nature because of its crystal structure and the mechanical
and Li for interaction with thermal neutrons, a combined processing it undergoes during the manufacturing.
7
use of Li and Li enriched thermoluminescence (TL) Hence, for investigating realistic failure simulation the
7
6
detectors gives clear estimation of gamma and neutron consideration of realistic anisotropic material behaviour
doses in the mixed field of gamma and neutron. Based is very important. The numerical studies conducted to
on this fact, suitability of LiF:Mg,Ti (MTS-6: 95.62% study the effect of Zr-2.5% Nb anisotropy on notch stress
6
6 Li and 4.38% Li) and LiF:Mg,Ti (MTS-7: 99.993% triaxiality and stress intensity factor in a tension test
7
7
7 LiF and 0.007% LiF) thermoluminescence detectors specimen showed that stress triaxiality for anisotropic
6
was studied for thermal neutron dose mapping around model is higher than the isotropic material (Fig. 7.24 (a)
paraffin wax moderated 5Ci 241 Am-Be neutron source. and (b)). This indicates early prediction of crack initiation
The calibration source and facilities (Thermal neutron with anisotropic material model compared to isotropic
flux standard facility and gamma standard source material model. Another numerical study conducted on
facility) of IGCAR, Kalpakkam were used for irradiation the development of residual stress in a cylinder made
purpose. Unlike the traditional methods which make from Zr-2.5%Nb observed that during the auto-frettage,
use of calibration curve obtained with gamma field to the residual stress obtained for the two-materials models
provide information on gamma equivalent neutron were different (Fig. 7.24(c) and (d)).
Fig. 7.24(a) &(b) : Plot of Stress Triaxiality along remaining Ligament for (a) 2.5 mm Notch Radius and (b) 5 mm Notch Radius
AERB Annual Report 2019 93